Interlock System Access Arrangements
To safely access equipment with an interlock system there
are many ways to interlock such systems depending on the amount of switches,
valves and other devices to be locked out, and the quantity of access ways
into the equipment to be protected. Following are some examples. These
examples can be expanded and incorporated into any interlock system.
- One single key interlock and one access Interlock.
Lock switch open and open access way - key cannot be removed until access
is locked closed, this prevents re-energizing equipment with access way
open.
- Pro - simple and low cost.
- Con - only for the simplest of equipment and systems.

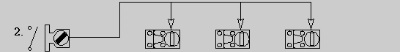
- One single key Interlock and multiple access Interlocks.
Lock switch open and open one of many access ways.
- Pro - low cost, only one key in system.
- Con - only one access way can be opened at any given time.
- One multi-key Interlock and an equal amount of access points.
Lock switch open and obtain all the keys for all the access ways.
- Pro - allows for all access points to be available for workers and technicians at one time saving money and time during shutdown periods.
- Con - higher initial cost. Maximum quantity of keys on switch limited to six.
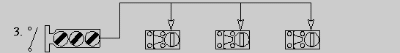
- One single key Interlock and multiple access Interlocks with an
operator's hold off key for each access interlock to prevent system reversal
(re-energizing) without the operator's hold off key.
- Pro - lower cost, hold off key is an additional safeguard for operator
- Con - only one access way can be opened at any given time.
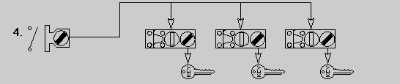
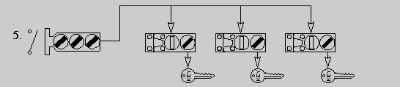
- One multi-key Interlock and an equal amount of access points with an
operator's hold off key for each access interlock to prevent system reversal
(re-energizing) without the operators' hold off key. Lock switch open and
obtain all the keys for all the access ways opening each door releases a hold
off key.
- Pro - allows for all access points to be available for workers and technicians at one time saving money and time during shutdown periods. Hold off key is an additional safeguard for operator
- Con - higher initial cost. Maximum quantity of keys on switch limited to six.
- One single key Interlock and multiple access Interlocks with a daisy chain
access sequence. Allows all access ways to be opened in a predetermined
sequence.
- Pro - allows for all access points to be available for workers and technicians at one time saving money and time during shutdown periods.
- Con - higher initial cost. Access ways must be opened and closed in a predetermined sequence.
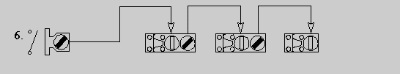
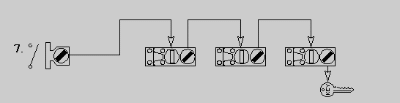
- One single key Interlock and multiple access Interlocks with a daisy
chain access sequence, with an operator's hold off key at the last access
interlock to prevent system reversal (re-energizing) without the operator's
hold off key. Allows all access ways to be opened in a predetermined
sequence, and release a hold off key.
- Pro - allows for all access points to be available for workers and technicians at one time saving money and time during shutdown periods. Hold off key is an additional safeguard for operator. Unlimited amount of access ways.
- Con - higher initial cost. Access ways must be opened and closed in a predetermined sequence.
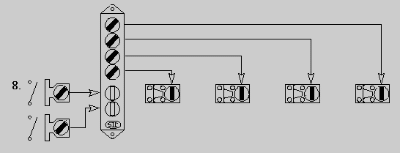
- Multiple key Interlocks and multiple access points, utilizing a key
transfer interlock. Operator locks out multiple related equipment obtains all
required keys. Deposits keys into transfer interlock, thereby releasing
multiple access keys to open some or all access ways.
- Pro - allows for all access points to be available for workers and technicians at one time saving money and time during shutdown periods. Unlimited amount of access ways. Unlimited amount of locked out devices. Greatest amount of flexibility.
- Con - higher initial cost.
|


![]() Home
Home
![]() Products
Products
![]() Schemes
Schemes
![]() Info
Info
![]() Forms
Forms
![]() Contact
Contact
![]() Site Map
Site Map
![]() EMail
EMail